Introduction
Pregnancy is a beautiful journey, but it can also come with its share of challenges. One such challenge is gestational diabetes, a condition that develops during pregnancy and can bring about feelings of fear and uncertainty. However, with the right tools, knowledge, and support, gestational diabetes can be effectively managed to ensure the health of both mother and baby. One of the most reliable tools available today is Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM). In this blog, we’ll explore how CGM can help manage gestational diabetes, the benefits of using these devices, and practical tips for maintaining a healthy pregnancy.
What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that typically develops during the second or third trimester of pregnancy, usually between the 24th and 28th weeks. Like Type 2 diabetes, it occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to its effects. Insulin is the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels, and when it’s not functioning properly, blood sugar levels can rise, potentially leading to complications.
Many women with gestational diabetes may not experience noticeable symptoms, but some common signs include increased thirst and frequent urination. If left unmanaged, gestational diabetes can pose risks to both the mother and the baby, such as preterm birth, high birth weight, and an increased likelihood of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Who is at Risk for Gestational Diabetes?
While the exact causes of gestational diabetes are not fully understood, certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing this condition during pregnancy. These risk factors include:
Age: Women over the age of 35 are at higher risk.
Family History: A family history of Type 2 diabetes can increase the chances.
Ethnicity: Women of African, Arab, Hispanic, Asian, Indigenous, or South Asian descent have a higher risk.
Obesity: A BMI of 30 or higher is a significant risk factor.
Previous Gestational Diabetes: A history of gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy increases the risk.
Large Baby: Delivering a baby weighing over 4 kilograms (approximately 8.8 pounds) in the past.
PCOS: Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are more likely to develop gestational diabetes.
Understanding these risk factors can help expectant mothers take proactive steps to manage their health and reduce the likelihood of complications.
How to Manage Gestational Diabetes Effectively
Managing gestational diabetes involves a combination of monitoring blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy diet, and staying physically active. Here’s how you can use modern CGM technology and other practical strategies to stay healthy during your pregnancy.
1. Monitoring Glucose Levels with CGM
The cornerstone of managing gestational diabetes is closely monitoring blood sugar levels. High blood sugar can lead to complications for both the mother and the baby, while low levels can result in hypoglycemia. According to Diabetes America, the target glucose levels for pregnant women with gestational diabetes are:
Before meals: Below 5.3 mmol/L
One hour after eating: Less than 7.8 mmol/L
Two hours post-meal: Under 6.7 mmol/L
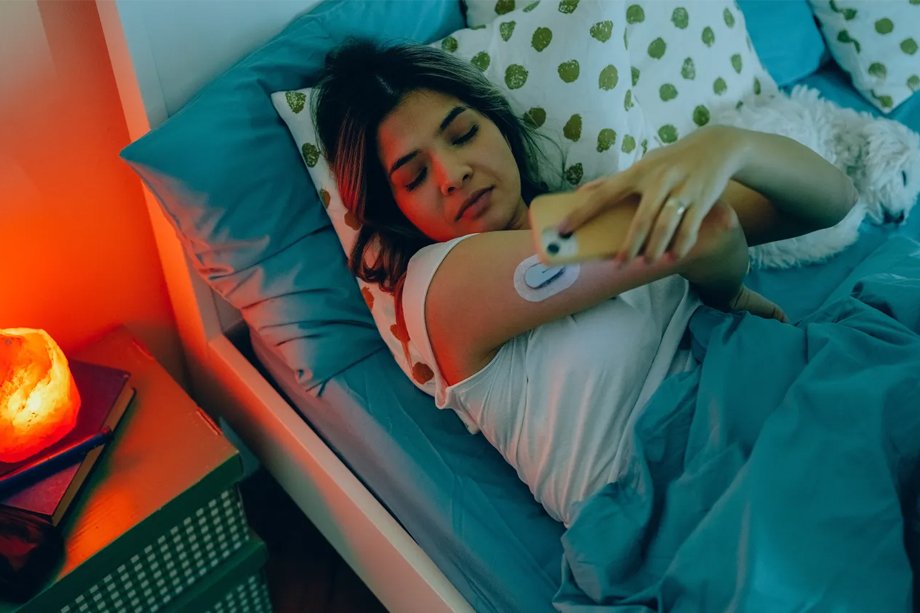
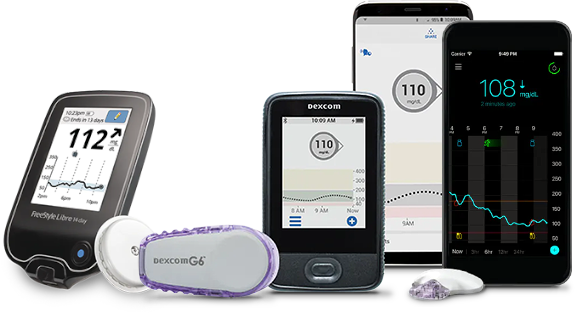
This is where Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems, such as the Dexcom G7 or Freestyle Libre 2, come into play. These advanced devices provide real-time glucose readings without the need for routine fingersticks. They continuously track glucose levels and can alert you when your levels are too high or too low, allowing you to take timely corrective actions. This makes it easier to stay within your target range and maintain a healthy pregnancy.
2. Eating a Balanced Diet
A healthy diet is crucial for stabilizing blood sugar levels. Unmanaged gestational diabetes can harm both the mother and the baby, so it’s essential to get your diet right. Consulting with a registered dietitian to create a personalized meal plan is a great starting point.
Here are some general dietary tips:
Choose Low-GI Foods: Foods with a low glycemic index (GI) help maintain steady glucose levels.
Balance Your Plate: Fill half your plate with non-starchy vegetables, a quarter with lean proteins, and the remaining quarter with whole-grain carbohydrates.
Avoid Sugary Drinks: Stick to water as your main beverage and avoid sugary drinks that can cause blood sugar spikes.
By monitoring your glucose levels before and after meals, you can identify which foods work best for you and make adjustments as needed.
3. Staying Active
Regular physical activity is another key component of managing gestational diabetes. Light-to-moderate exercises, such as walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga, can be highly beneficial. Aim for at least 150 minutes of activity per week, spread over three or more days. Exercise helps control blood sugar levels, promotes healthy weight gain during pregnancy, and can even improve your overall mood and energy levels.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, managing gestational diabetes becomes much easier and more effective with the help of CGM technology. These advanced devices provide real-time updates on your glucose levels, ensuring you stay within a healthy range, even during activities like exercise. This means you can adjust your routine if your glucose levels drop too low, without compromising your workout or daily activities. Combined with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper medical guidance, CGM technology empowers you to take control of your health during pregnancy, safeguarding both you and your baby.
If you’re ready to take the next step in managing gestational diabetes with the support of CGM devices, visit Med Reliance DME LLC. We can help you check your insurance coverage and provide CGM devices, ensuring you have everything you need for a healthy and worry-free pregnancy.